This article is an expansion and comment on author Shitao Liu’s paper that provides a trend strategy that uses portfolio utility optimization.
Designed for U.S. stocks, this approach leverages momentum and portfolio optimization to deliver superior risk-adjusted returns.
The Concentration Effect
The U.S. stock market isn’t a level playing field. Research, including Hendrik Bessembinder’s study of wealth creation from 1926 to 2019, reveals a stark reality:
Most stocks underperform, while a handful of outperformers—like the "Nifty Fifty" of the 1960s or the "Magnificent 7" of the 2020s—drive the bulk of returns.
Industry reports from Thornburg Investment Management and FS Investments reinforce this, noting that in 2023, just 10 stocks accounted for 75% of the MSCI U.S. Index’s gains.
This concentration effect suggests that identifying and investing in these “winning horses” could unlock outsized returns.
Liu’s strategy builds on this insight, aiming to systematically select stocks with strong momentum—those trending upward—and optimize a portfolio around them. But how does it work in practice?
The Strategy
Liu’s "Ride the Right Horse" strategy is a blend of trend-following and rigorous portfolio optimization, executed daily. Here’s a step-by-step look at how it operates:
First, calculate market-implied risk. For each stock in a pool (S&P 500 and NASDAQ 100 constituents; for other markets, we’ve to test this as well, but for the timing being, let’s stick to US), calculate its market-implied risk over the past year:
Compute the median across all stocks and market risk from the SPY ETF (a proxy for the market).
If the broad market is having a negative excess return over the past trading year, it is a somewhat clear indicator that we should not position ourselves in the market.
Selecting Momentum Stocks
If Delta market > 0, form a candidate pool of stocks with delta > 0, indicating positive momentum.
In other words, short term moving average is higher than last price and short term moving average is higher than long term moving average.
The portfolio weights are then optimized daily using mean-variance optimization, balancing expected returns against estimated covariance while capping any single stock’s weight at 10% for diversification.
Use historical prices from the past year to estimate expected returns and the covariance matrix.
Executing Trades
Solve an integer programming problem to adjust share counts based on current prices and net asset value, accounting for transaction costs (0.4 bps + $0.0015 per share).
Apply a profit-taking rule: Hold a stock only if its last price exceeds its 5-day moving average, and the 5-day average exceeds the 30-day average.
This methodical process combines momentum investing—capitalizing on stocks’ tendency to persist in performance—with portfolio optimization rooted in Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT).
Guding principle is - the stocks with strong past performance are likely to continue outperforming, as documented by Jegadeesh and Titman (1993) and Asness et al. (2014).
MPT, pioneered by Harry Markowitz, balances return and risk, enhanced here by daily adjustments and diversification constraints.
This synergy drives the strategy’s ability to “ride the right horse” while managing downside risk.
Liu tested the strategy using historical data from 2013 to 2024, pitting it against the SPY ETF and an equal-weighted portfolio. The results are striking:
These metrics suggest the strategy not only outperforms but does so with greater stability—a holy grail for investors.
Ablation Study
To understand what makes the strategy tick, Liu conducted an ablation study. This works by systematically removing or changing individual components—such as a profit-taking rule or a diversification parameter—and then observing how these changes affect the overall performance.
Those are as under:
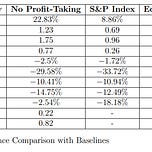
Profit-Taking Rule
Without It: CAGR jumps to 22.83%, but drawdown rises to 29.58%.
Insight: The rule caps upside but protects against volatility.
Diversification Parameter (d)
d = 0.05 (5% max): CAGR drops to 7.61%, drawdown shrinks to 11.74%.
d = 0.25 (25% max): CAGR rises to 15.27%, drawdown hits 28.5%.
Sweet Spot: d = 0.1 balances return and risk.
Risk Parameter
Median slightly outperforms fixed values (e.g., delta = 1), adapting better to market conditions.
Transaction Costs
At 1 bp per trade, CAGR holds at 11.48%; at 10 bps, it fails to beat SPY.
Takeaway: The strategy thrives under realistic cost assumptions.
By targeting stocks with positive (delta), it rides proven trends. Daily optimization and moving average filters mitigate losses. The median adjusts risk dynamically.
For financial professionals, this strategy offers actionable insights. Firstly, a rules-based approach reduces emotional bias. Secondly, integer programming and cost considerations make it implementable. And lastly, lower drawdowns appeal to conservative portfolios.
Note - Attached audio discussion is AI generated. So be careful while taking the audio for accuracy.